If you have ever used TPU 3D printer filament before, you might have had issues with a stringing mess created by the printer, or maybe bad layer adhesion. This is often caused by moisture in the TPU filament, which typically happens when it is not stored in an airtight container or package. So let us try to understand this phenomenon better, and how to fix the issue. Enjoy!
What Is TPU?
In short, TPU filament (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) is a popular filament among hobbyists and pros alike to work with in their 3D printers, and is generally considered a user-friendly and cost-effective soft material. It is valued for its unique combination of rubber-like flexibility and plastic-like processability, which is ideal for use in a wide variety of situations and applications.
However, it also happens to be hygroscopic, meaning that it will pick up moisture from the air. You should be aware of this, because it not only impacts the way you should be dealing with the material, but also how much you need to take into consideration when storing your used TPU 3D printing filament.
If you want to learn more about TPU properties, answering questions such as “Is TPU Waterproof?” we have already written another article covering the filament in more detail here: TPU Filament Guide.
TPU’s Hygroscopic Properties
As mentioned above, TPU has hygroscopic properties, which make the material susceptible to moisture absorption. This is due to the overall chemical structure of the filament, and not something that can be avoided with TPU.
On a high level, you can think of TPU as a blend of hard and soft segments, which together provide both strength and flexibility to your 3D printed objects. However, this also creates “holes”, which in scientific terms are called polar sites that allow hydrogen to bond with the material.
Below, we have highlighted the TPU’s hygroscopic properties, and what the molecular structure looks like for the more scientific readers.
Strong Polar Chemical Bonds
- Urethane Linkage (-NH-COO-): It is the basic chemical bond that constitutes the polymer backbone, which has a high polarity.
- Carbonyl (C=O) and Amide (-NH-) Groups: These groups are very polar and have a natural affinity to water molecules.
Hydrogen Bonding Mechanism
- Water molecules (H₂O) are also strongly polar.
- Oxygen (O) and Nitrogen (N) atoms on the TPU chain form strong intermolecular hydrogen bonds with hydrogen (H) atoms in water molecules, effectively “trapping” them.
How to Identify Moist TPU Filament
Alright, now that you know TPU can absorb moisture, how do you figure out whether it is good for use, or whether you need to dry it before using in your 3D printer? Luckily, there are a few things you can do to identify wet filament symptoms. Below we have listed 3 different signs so you can identify moist TPU filament.
- Hearing cracking or popping noises from the hot-end while printing.
- Formation of small bubbles inside the filament or defects on the surface of a printed part or model.
- Wet or moist filament tends to feel tacky and/or brittle, losing some of its flexibility.
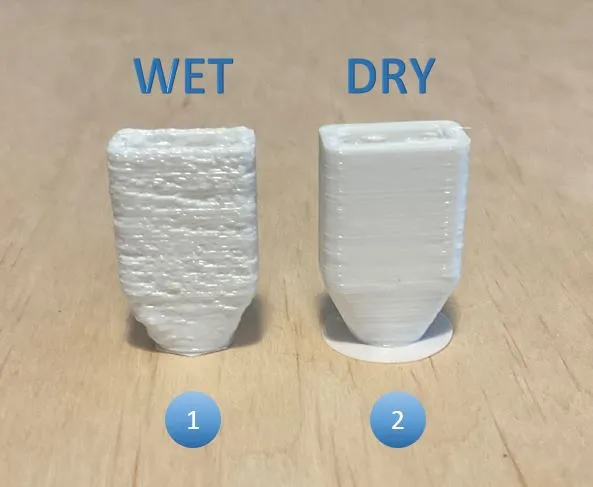


The most important point is number 3, that can be tested before you start printing with the filament. So try handling the TPU filament in your hand, and see if it feels sticky, or whether it might It feels stiffer and bounces back faster when bent than you remember. As you know, TPU is a rather flexible filament, so you should be able to bend it quite a bit before it snaps.
How to Prevent and Dry Moist TPU Filament
The best way to avoid any type of moist TPU 3D filament in your prints, is to store all your materials properly. Of course, if moisture has already occurred, we can also remedy it.
Generally speaking, there are two different methods that yield the most consistent results, while maintaining the flexible 3d filament properties.
Proper Storage
- Use airtight, moisture-barrier bags, such as vacuum-sealable bags with desiccant.
- Use dry storage containers.
There are also other options you can use, such as normal plastic bags with zip ties or tape ensuring a solid seal, although these are not as reusable and practical for frequent printing, and also more prone to failure.
Dry Filament
If you believe your TPU filaments might have trapped some moisture inside it, no amount of correct storage can fix the issue. You will instead need to manually extract the water by drying your TPU filament at home.
- Ideally you would use a professional filament dryer, as it is the most effective method. In this case the recommended TPU drying temperature settings are 50–60°C for 4–6 hours.
- Alternatively, you can sometimes get away with using your conventional oven, although this is more of a DIY hack and difficult to truly control the precise temperature. So be careful if you try this at home.
If you are printing quite often at home, it might be worth investing in a special filament drying machine, as they are becoming cheaper now that more people are using them, and can save you quite a bit of money and time in the long run.
On the other hand, if you would rather save your money, sometimes you can find 3D printing workshops and makerspaces in larger cities, that will have one you can use for a small fee, or even for free on occasion. This can be a good way to achieve dry filaments and test out the dry machines, and maybe even connect with other hobby enthusiasts!
More tips for storing and drying filament: How to Dry And Store 3D Printer Filament.
Conclusion
In the end, TPU is both a strong and flexible 3D printer filament, but the downside is that its hygroscopic properties make it prone to moisture absorption, which can quickly ruin a print. But this isn’t a lost cause.
If you know how to identify the warning signs of a wet filament and recognize that adequate filament storage is your first line of defense, the problem can become much easier to deal with. If moisture enters your filament, bear in mind that a filament dryer is worth the investment to guarantee your 3D prints will be reliable and of quality. A little preventative maintenance will keep your all-purpose TPU filament ready for your next great project.