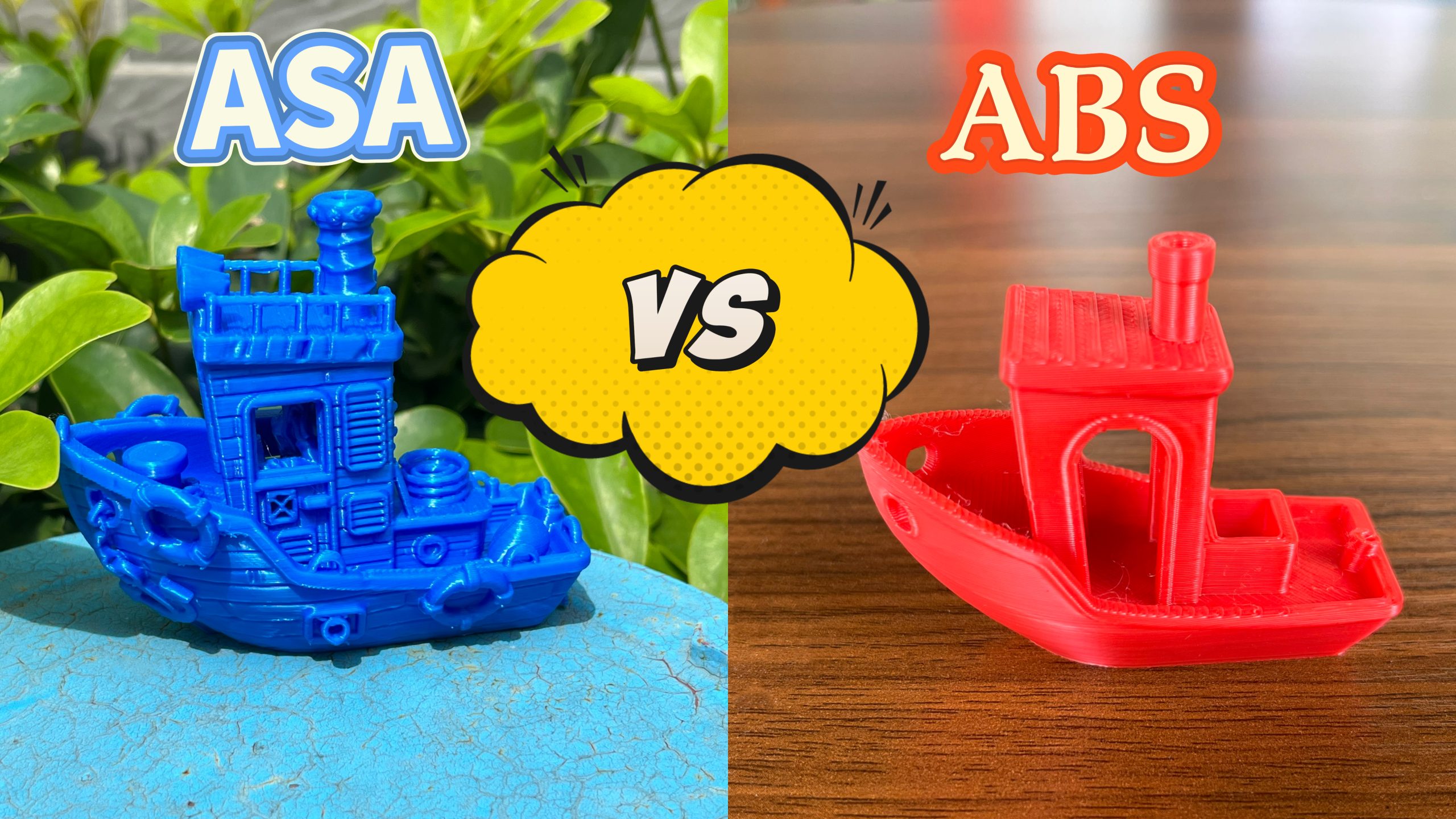
Whether you are printing many different prints, or just looking for the best value, researching more about ASA and ABS filament is a great way to set yourself up for success. So today we will be looking at which is the best 3D printer filament as a general all-around material in terms of pure value.

ASA vs. ABS Filament: Composition
Before diving into details, let us first start with a few basics about ABS and ASA 3D filament. They are both what is known as ternary copolymers, which is a fancy way of saying both have 3 key monomers in their composition. However, the specific composition is slightly different, which provides different effects in your 3D printer.
ABS filament uses butadiene, which makes the filament and 3D prints tougher, and also provides impact resistance. ASA filament, on the other hand, uses acrylate as the third monomer, which improves weather and UV resistance, but makes the filament slightly less able to resist impacts (around 15% less resistant than ABS).
Both the ASA and ABS printer filaments use acrylonitrile and styrene in their compositions. This provides great chemical resistance and rigidity to your models, while also making them easy to process once printed. This means that the main difference is that ASA is great for outdoor use, while ABS is great for heavy duty prints.
ASA vs. ABS: Properties
Next, let us take a closer look at ABS vs. ASA filament properties in a table to get a quick and easy overview. As you can see below, they are both decent at heat and chemical resistance, with the main differences being in terms of strength, UV and weather resistance.
| Property | ASA | ABS |
| Strength | High tensile strength | Slightly higher impact strength |
| UV Resistance | Excellent (no yellowing) | Poor (degrades in sunlight) |
| Weather Resistance | Excellent (resists moisture, heat, cold) | Poor (cracks, warps outdoors) |
| Heat Resistance | Good (slightly better than ABS) | Good (softens at ~100°C) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good (resists oils, acids) | Good (but weaker than ASA) |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, matte | Glossy, prone to warping |
ASA vs. ABS: Printing
When it comes to printing with these two filaments, there are some slight differences in terms of settings, the optimal environments and potential issues. Again, we have opted for a table to quickly list the differences between ASA and ABS filament. For instance, look at the difference between ASA and ABS print temperature in order to see how the different compositions change the printing settings.
| Factor | ASA | ABS |
| Printing Temp. | 240–260°C (5–10°C higher than ABS) | 230–250°C |
| Bed Temp. | 90–110°C (heated bed required) | 90–110°C (heated bed required) |
| Cooling | Gentle fan (10–20%) improves surface | Minimal or no fan (warp risk) |
| Enclosure | Recommended (reduces warping) | Required (prevents cracking) |
| Odor/Fumes | Strong fumes (ventilation needed) | Strong fumes |
| Adhesion | PEI or glue stick recommended | ABS juice or Kapton tape |
| Warping/Cracking | Less prone (better layer adhesion) | High risk (needs enclosed chamber) |
As you can see, ABS is more likely to warp or crack when being printed and thus it is recommended to use a 3D printer with an enclosed chamber for the best results, but cooling is not necessary for most cases. Both filaments do well with ventilation due to the strong ASA filament fumes, and the printing temperature of ASA plastic material is usually 5 to 10 ℃ higher than ABS.
ASA vs. ABS: Performance of Prints
Once you have printed your 3D prints with either ASA filament or ABS 3D printer filament, it is also important to consider the performance due to the different properties. Post-processing is a key factor for many people, and both materials do fairly well in this regard, with ABS being the slight winner due to its particles are relatively soft than ASA.
| Aspect | ASA | ABS |
| Durability | Excellent outdoor longevity | Strong but degrades outdoors |
| Post-Processing | Sanding, painting | Easier Sanding, acetone-smoothable smoothing |
| UV Stability | No degradation over time | Yellows, becomes brittle |
| Impact Resistance | Good (but ~15% weaker than ABS) | Excellent |
| Flexibility | Slightly more rigid | More flexible |


ASA vs. ABS: Applications
While we have already touched on applications earlier, let us look in more detail at the best uses for ABS plastic filament and ASA filament. The rule of thumb is that ABS is best for indoor parts, while ASA is a great option for prints used outside.
Digging a little deeper, we often see examples of ABS parts being used in functional parts. This is because ABS is more suitable for printing indoor engineering components, as it has high strength but is not weather-resistant. Examples include items such as gears, housings, dashboards, electronics enclosures or even toys due to their durability and the fact that they are easy to clean up and post-process.

ASA has the same mechanical properties and offers better UV resistance, weather resistance and color stability, making it more suitable for outdoor applications. ASA filament is thus often used for outdoor signs, garden tools, light fixture housings, and even bumpers for cars or bikes on larger printers. They are also used for drone bodies and RC cars as the UV-resistance means they will not fade or turn yellow as opposed to ABS 3D printing filament.
Learn more information about ASA filament: The Ultimate Guide to ASA Filament for Durable and Weather-Resistant 3D Printing.

Conclusion
In terms of service life, ASA 3D printer filament emerges as the big winner. It has superior weather resistant properties, makes for easy printing, and its long-term toughness makes it the smarter purchase for most applications, while it will cost a few dollars more initially. If your printed models are only designed to be used indoors and you desire the highest amount of strength and resistance possible, ABS remains a quality, economy-priced option. So here’s our tip: choose ASA for versatility and long-term life, and then choose ABS for budget ruggedness.